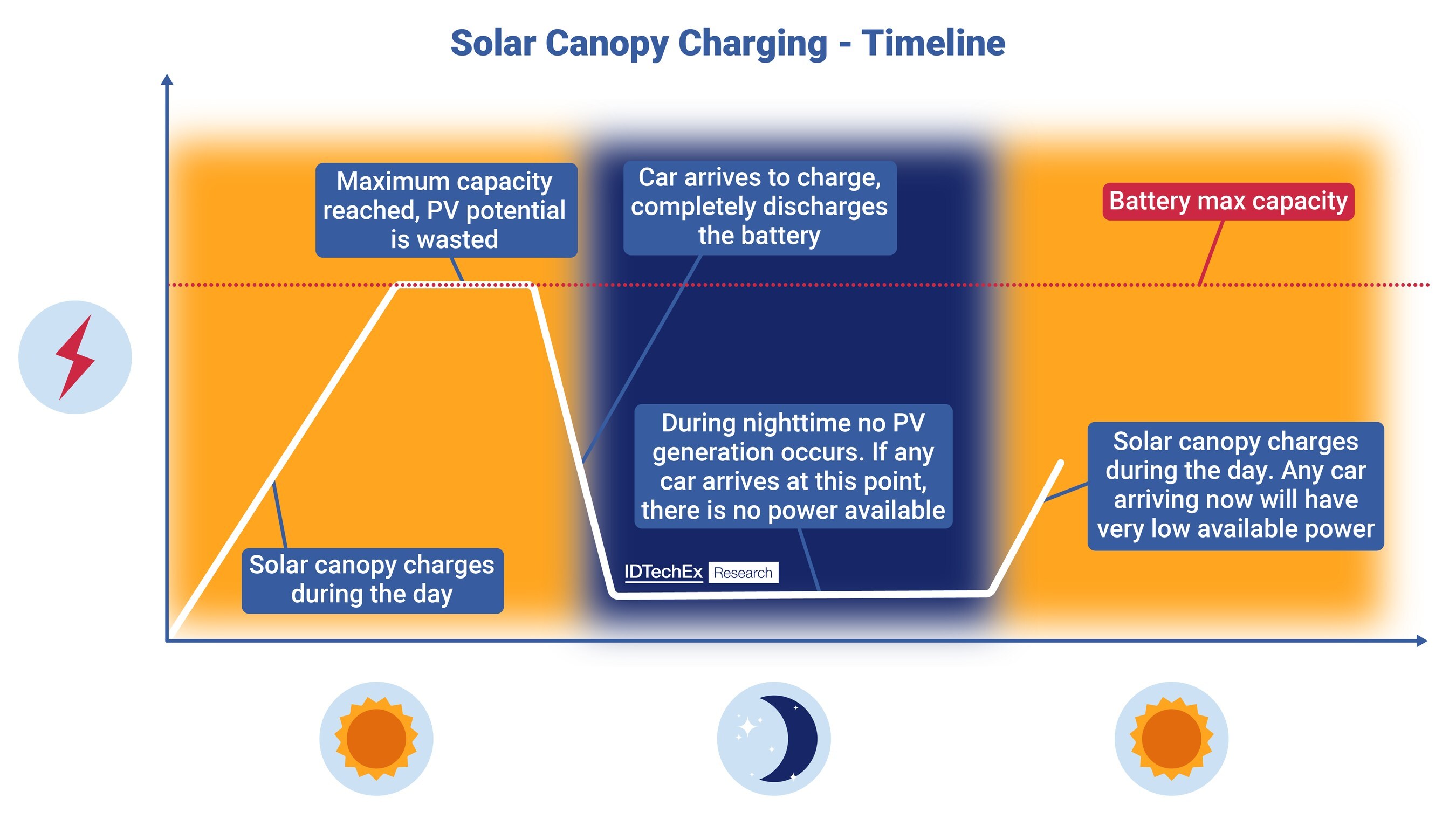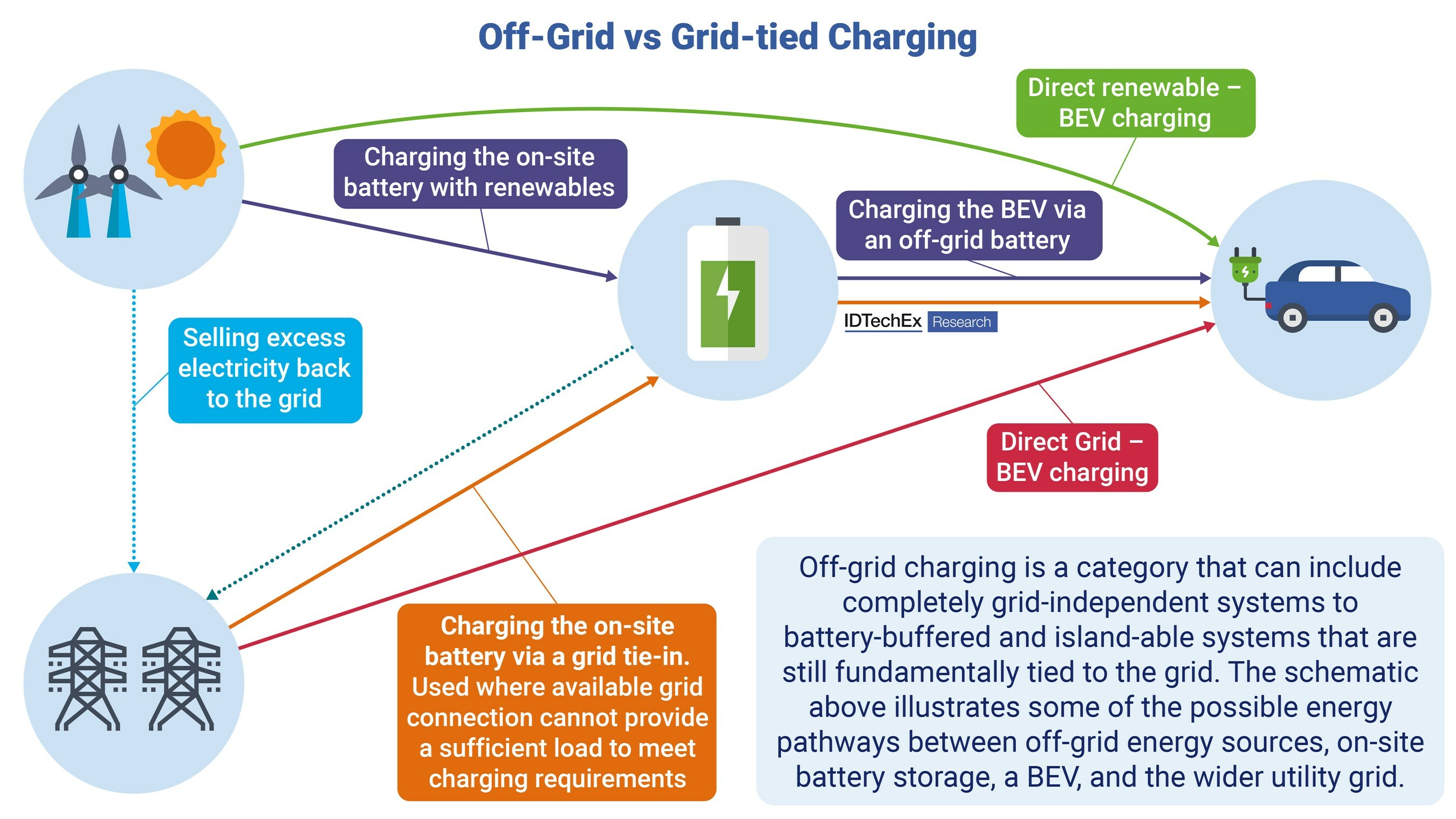
Off-grid charging bypasses the grid, drawing power from sources like solar or hydrogen. Solar canopies, a leading solution, offer shade and charging but have limitations. Their power generation is low, limiting charging speeds and making them unsuitable for high-powered fast charging.
Fuel cell generators, another option, use stored hydrogen to create electricity. They can operate 24/7 regardless of weather, unlike solar. However, sourcing clean hydrogen remains a challenge, and some types might have a higher carbon footprint than diesel generators.
Despite these challenges, IDTechEx forecasts significant growth for off-grid charging, particularly in sectors like construction and highway fast charging, with a potential market value of US$14 billion by 2034.
The report delves into key questions: Why is off-grid charging needed? How do technologies compare? Who are the key players? It also analyses supply chains, emissions, costs, and future market growth.
This report offers market forecasts, player profiles, and company lists, making it valuable for anyone seeking in-depth knowledge of this emerging and crucial industry.
To find out more about the IDTechEx report "Off-Grid Charging for Electric Vehicles 2024-2034: Technologies, Benchmarking, Players and Forecasts", including downloadable sample pages, visit www.IDTechEx.com/OffGridEV.