At the launch event, Wang Zhiwu, president of Huawei Smart Charging Network Domain, comprehensively interpreted these trends from technology and industry perspectives.
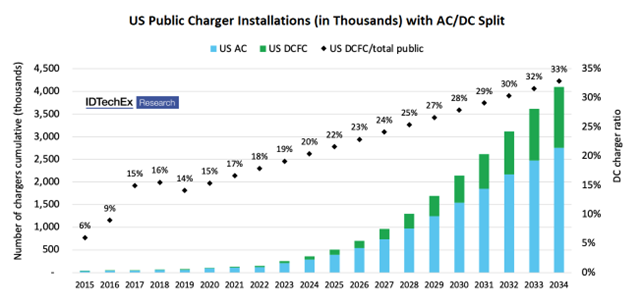
He highlighted that EVs have exceeded growth expectations over the past three years. In the next decade, the number of EVs on the road is expected to increase tenfold, with an eightfold increase in EV charging demand. As the immature charging network remains the primary pain point of the entire EV industry, building a high-quality charging network will accelerate the new electric vehicle (NEV) penetration and boost the local industry and ecosystem.
As the world accelerates toward mobility electrification and carbon neutrality, Huawei released its trends study, based on in-depth insights and aspirations for high-quality charging anywhere, together with partners in the industry.
1) High-Quality Development. The industry collectively strives for high-quality development of charging networks through unified planning and design, unified technical standards, unified government supervision, and unified O&M for users.
2) Comprehensive Ultra-fast Charging. With the maturity of third-generation power semiconductors and high-C-rate traction batteries that use materials such as silicon carbide and gallium nitride, EVs are steering toward the high-voltage ultra-fast charging domain. It is predicted that high-voltage ultra-fast charging vehicle models will account for more than 60% of the total vehicle models in 2028.
3) Optimal Experience. With NEVs rapidly gaining popularity, passenger vehicle owners replace commercial vehicle owners as the main users, and therefore the mainstream charging preference shifts from low cost to optimal experience.
4) Security and Trustworthiness. With the continuous penetration of NEVs, the industry's data volume explosion poses great challenges in ensuring electrical safety and cybersecurity. A secure and trustworthy charging network features no privacy leakage, no electric shock, no fire accident, and no service breakdown.
5) Vehicle-Grid Interaction. As the grid is facing greater randomness in power generation and consumption, the charging network will play a vital role in a renewables-dominated power system. Along with the growth path of business models and technologies, the vehicle-grid interaction will go through three key phases: one-way coordination, one-way response, and two-way interaction.
6) Power Pooling. Charging facilities are shifting from the integrated charger architecture to the power pooling architecture to meet the charging power requirements of different vehicle models at different SOC levels. In addition, intelligent scheduling meets the charging requirements of all vehicle models and contributes to improving grid power utilisation, reducing site construction costs, and supporting the long-term evolution of vehicles.
7) Fully Liquid-Cooled Charging. Fully liquid-cooled charging facilities, in comparison to air-cooled or semi-liquid-cooled ones, boast a lower annual failure rate of less than 5‰, a lifespan of over 10 years, and adaptability to various environments, slashing O&M costs.
8) DC Power Normal Charging. The future campuses with integrated parking and charging, the small-power DC charging solution will be more popular and applied on a large scale. Compared with traditional AC chargers, the DC charging solution will achieve optimal charging, higher grid power utilisation, and long-term evolution to V2G interaction.
9) Campus Microgrid. Future campuses are likely to integrate PV systems, ESSs, chargers, loads, vehicles, and cloud systems through unified cloud-based management to achieve higher economic benefits from electricity and grid friendliness.
10) All Intelligence. The lack of an advanced digital charging network has led to isolated management of the networks, stations, devices, and vehicles. This will change as these isolated parties are integrated into an intelligent charging network to facilitate vehicle-charger collaboration, vehicle-grid interaction, and digital O&M.
Huawei says it stands at the forefront of a promising industry, ready to embrace a future filled with immense opportunities. The company will continue to increase R&D and technical investments to build smart charging network solutions that are favoured by vehicle owners, trusted by operators, and friendly to the grid. Huawei says it will also work with partners such as automakers and operators to build an ecosystem and provide high-quality charging anywhere for vehicle owners to travel at will.