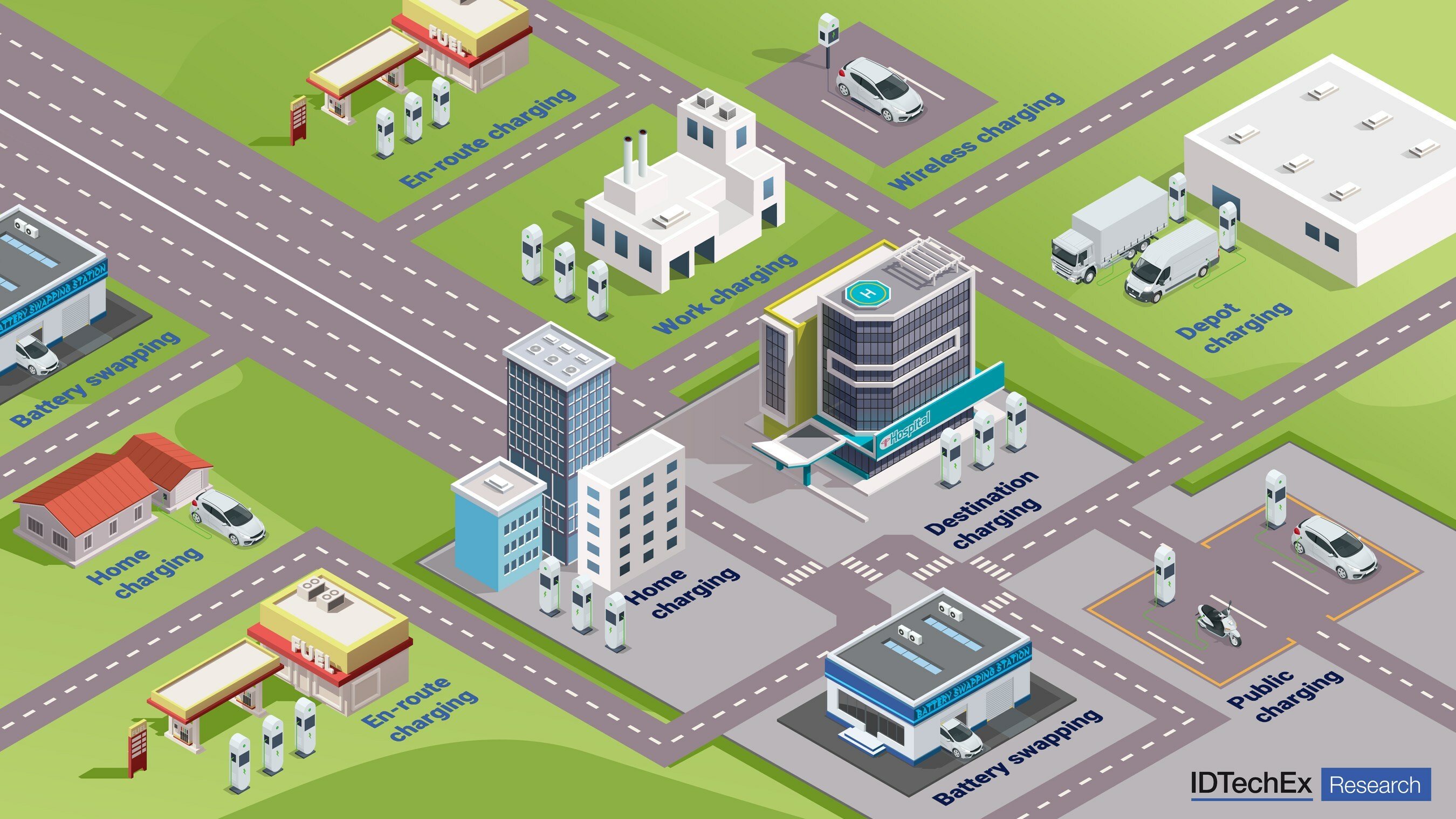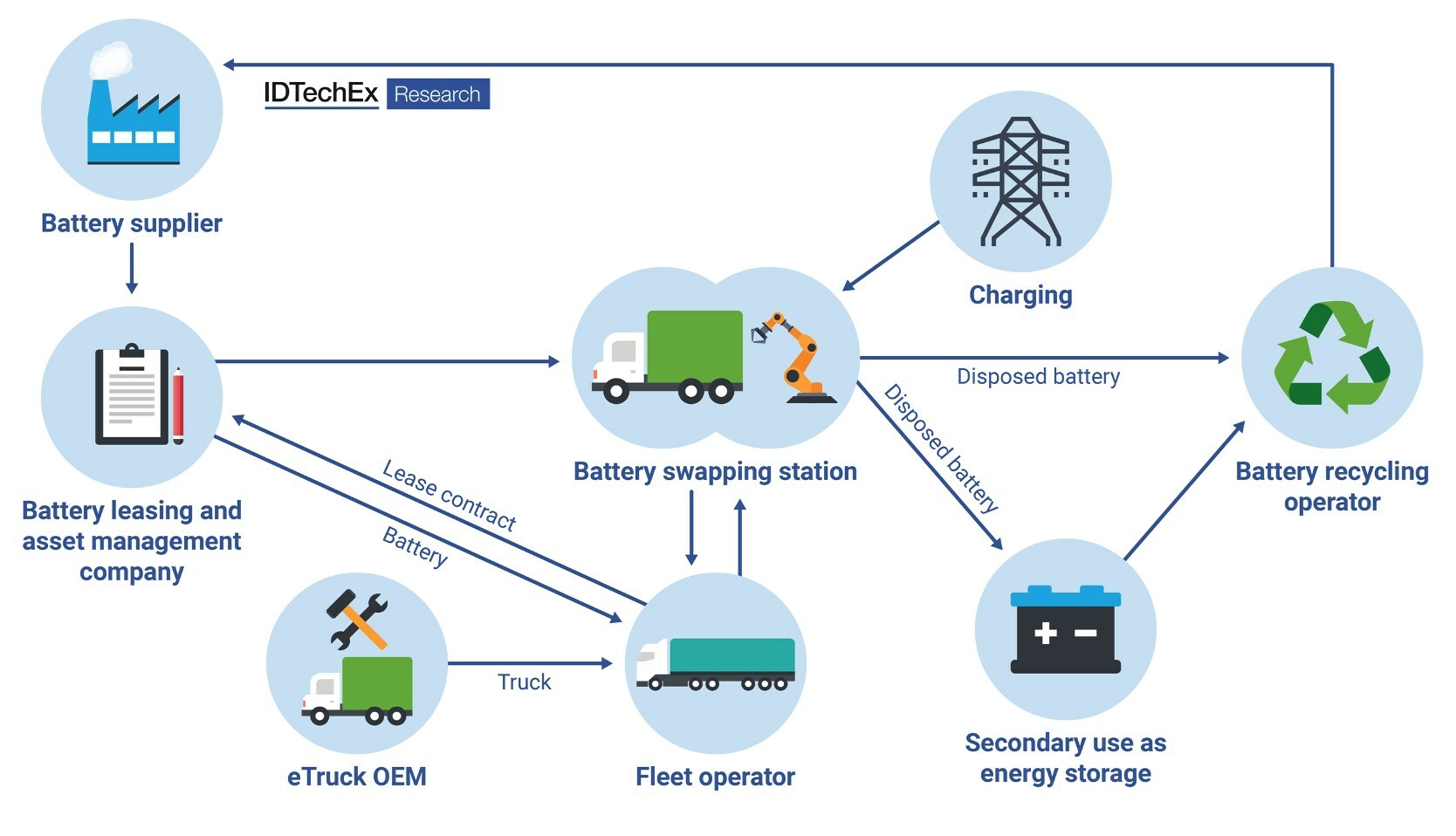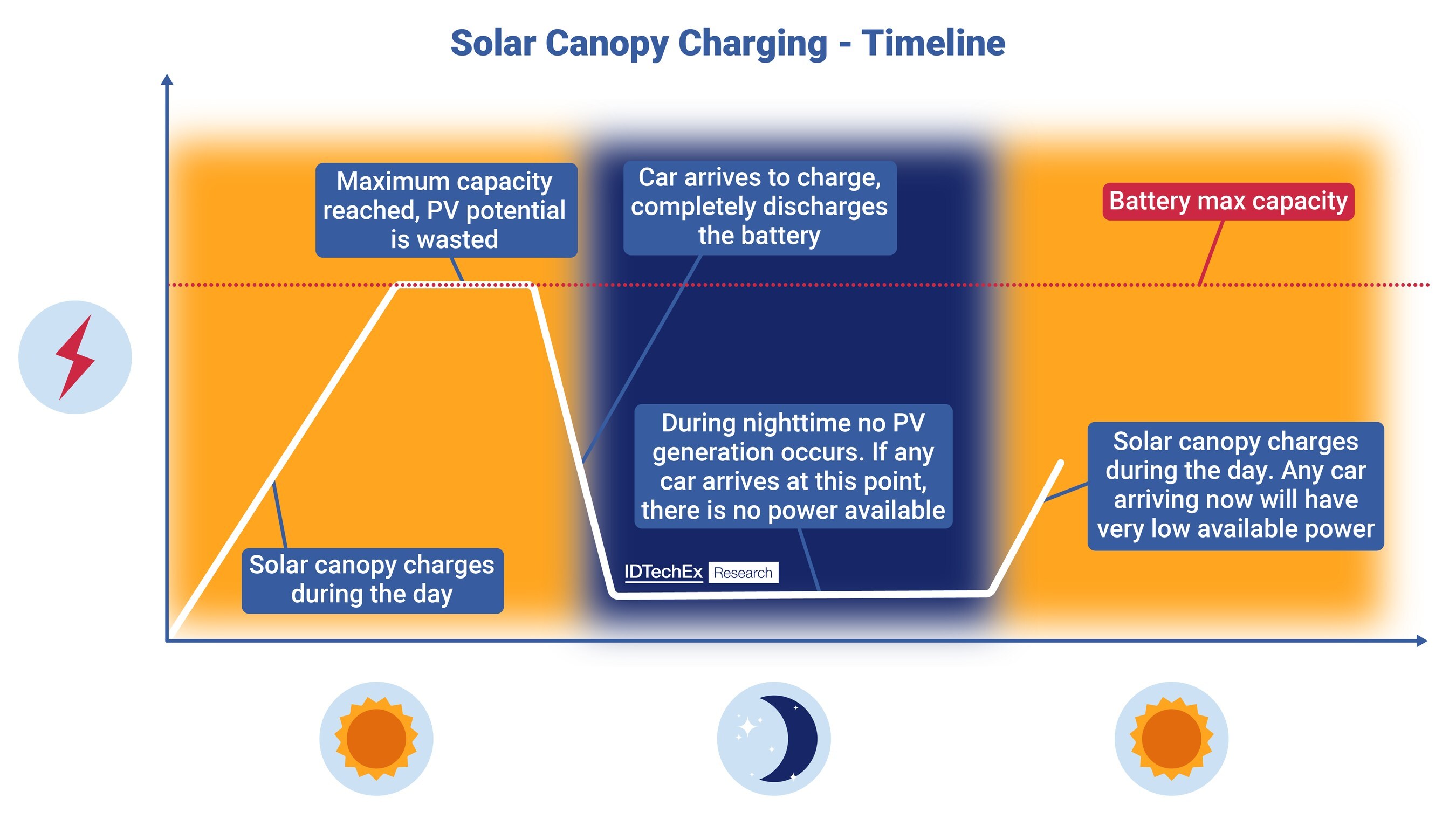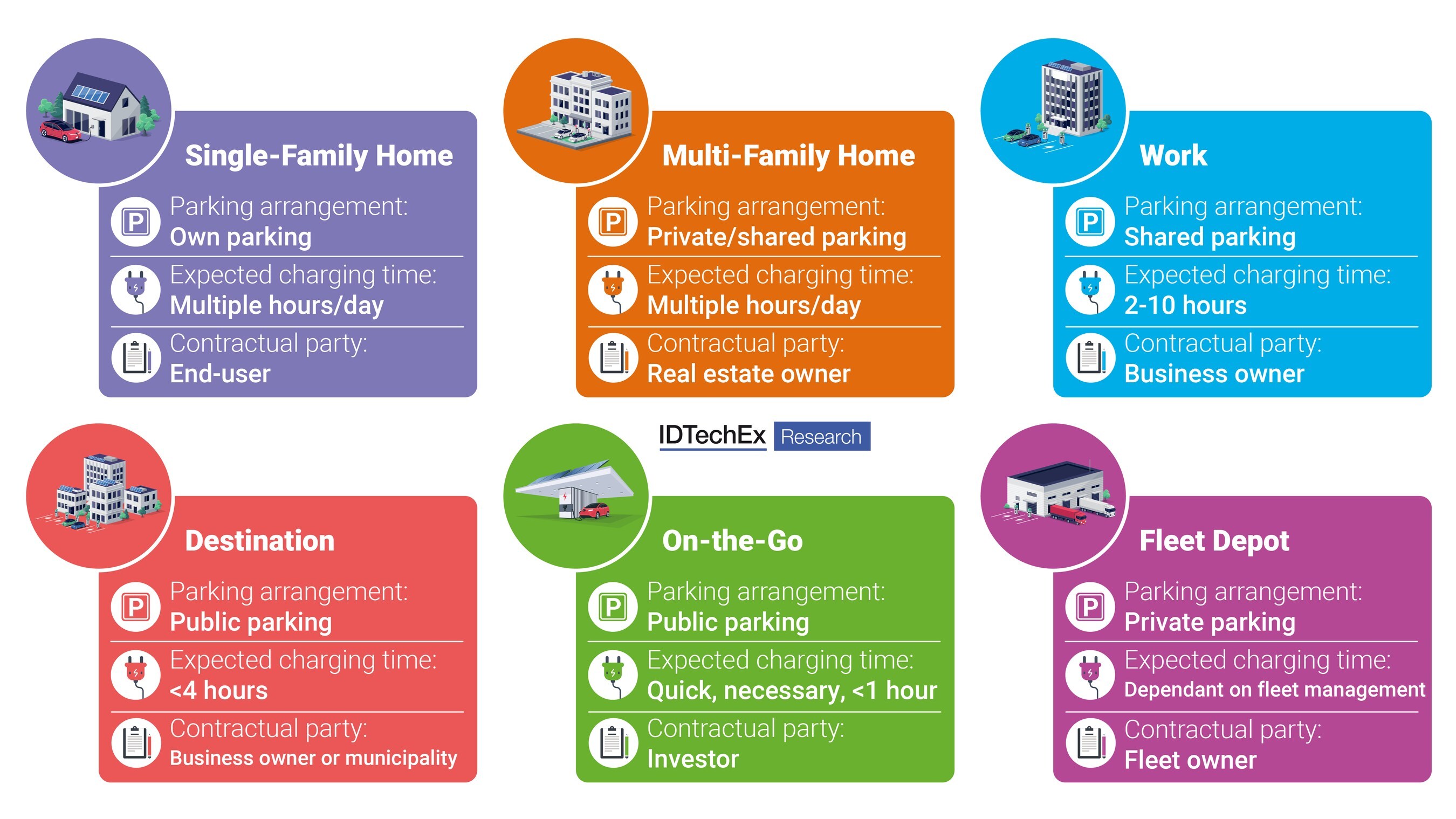
It finds that roughly 72% of existing public chargers globally were concentrated in China by the end of 2023, with approximately 77,000 new public charging units being installed every month.
Shazan Siddiqi, senior technology analyst and author of the report explains, "Charging has expanded enormously, but utilisation is low – around 5% for public chargers in 2024, dropping from 10% in 2023. The average Chinese charging post has a charge rate of 30 kW, charges 39 kWh per day, for around 77 minutes per day – this implies around 2-3 customer sessions per day. In the US, however, L3 (DCFC) utilisation is up 32%, growing from an average of 13% in July 2023 to 17% in June 2024. After rapid growth at the end of last year, utilisation appears to have stabilized at 16-17% in the first half of 2024."
The EV charging market is characterised by high capital expenditure (CapEx) and low profit margins, creating a challenging environment for smaller players. The market is ripe for consolidation, with larger companies acquiring smaller, less profitable entities to scale up operations.
Innovations such as smart charging, which balances grid demand and integrates renewable energy sources, are becoming more prevalent, enabling more sustainable and reliable charging options. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is also gaining traction, allowing EVs to feed energy back into the grid, thus providing additional value to both consumers and energy providers. The report plots how these technological developments are poised to play a pivotal role in the future of EV charging, making the infrastructure smarter and recognizing the value of EVs as distributed energy resources.